COVID-19 situation updates for week 30 (23-29 July 2023)
As of 29 July 2023, the global cumulative incidence of COVID-19 reached 768,638,185 reported cases and 6,969,134 associated deaths with a case-fatality ratio (CFR) of 0.91%. Meanwhile, the Eastern Mediterranean Region (EMR) has reported a total of 23,385,528 cases representing 3.05% of the global count, with 351,368 associated deaths (CFR 1.5%). Most countries in the Region are in the community transmission phase. This report doesn’t not represent an accurate COVID-19 situation in the EMR given that updates are not received from all 22 Member States regularly.
During epidemiological week 30 of 2023, a total of 298 lab-confirmed COVID-19 cases and 7 associated deaths were reported from 4 Member States (CFR: 2.4%). This indicates a 12% decrease and a 40% increase in the number of cases and deaths respectively compared to week 29. No updates were received from 18 Member States during week 30. The weekly number of cases has increased in almost all the reporting Member States except in Afghanistan which reported a 26% decrease in the number of cases compared to the previous week. The overall number of COVID-19-associated deaths also increased in the reporting Member States and no Member State reported a decrease in the number of COVID-19-associated deaths in week 30. A total of 34,435 COVID-19 laboratory tests were conducted in week 30 in 4 Member States (Positivity Rate: 0.87%) which indicates an 8% decrease in the number of tests compared to the previous week. This brings the cumulative number of COVID-19 laboratory tests in EMR to 449,094,863 since the start of the outbreak. The highest number of PCR tests were reported from United Arab Emirates (200,761,593; 44.7%), followed by the Islamic Republic of Iran (IR Iran) (56,996,521; 12.7%), and Saudi Arabia (45,484,848; 10.1%). The average positivity rate for the Region in 2022 is 4.1% (ranging from 0.3%-10.9%). WHO recommends a positivity rate of around 3–12% as a general benchmark indicating adequate testing, which was achieved in most countries of the Region.
Since the beginning of the outbreak, the country that has reported the highest number of total cases in the Region is IR Iran (7,612,935; 32.55% of the Region’s total), followed by Iraq (2,465,545; 10.54%) and Jordan (1,746,997; 7.47%). IR Iran also reported the highest number of total covid19-associated deaths (146,311; CFR 1.92%) followed by Pakistan (30,656; CFR 1.94 %) and Tunisia (29,423; CFR 2.55%). The lowest CFRs were reported by the United Arab Emirates (0.22%), Bahrain (0.22), and Qatar (0.13%) while the highest CFRs were reported by Yemen (18.07%) followed by Sudan (7.89%) and Syria (5.51%) respectively.
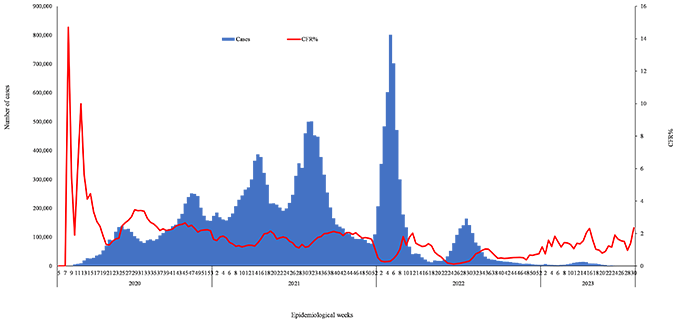
Figure 1: Epidemiological curve of COVID-19 laboratory confirmed cases and CFR, EMR, February 2020- July 2023
Supporting countries in the Region
The regional incident management support team continues to coordinate the response and provide technical support to countries and partners in the Region in the areas of coordination and partnership, surveillance, laboratory capacity, clinical management, infection prevention and control, risk communication, and community engagement, points of entry according to the International Health Regulations (2005), research, health systems, and essential health services among others. Furthermore, COVID-19 vaccination continues across the Region. The total number of doses administered so far in the 22 countries is 898,831,670 and the average coverage of the fully vaccinated population in the Region is 50%. The United Arab Emirates (98%), Qatar (97%), and Kuwait (77%) have reported the highest number of fully vaccinated coverage while Libya (18%), Syria (13%), and Yemen (3%) the lowest number of fully vaccinated coverage in the Region (Figure 2).
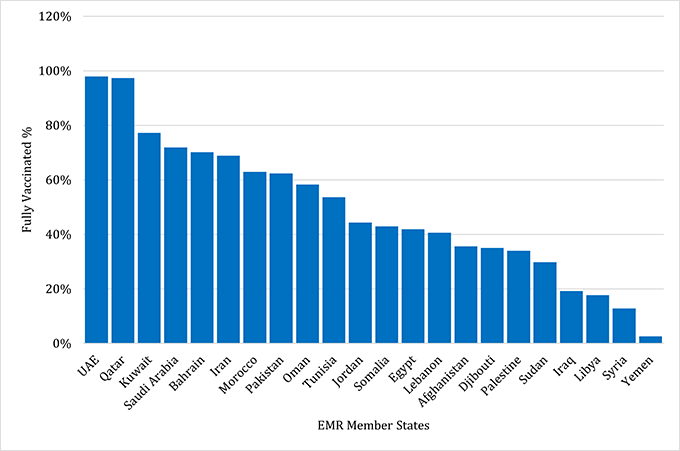
Figure 2: COVID-19 vaccine coverage by EMR Member States, July 2023
For more data from the Region, please visit the COVID-19 dashboard.
*The data on vaccination is obtained from several sources including media reports and country websites for ministries of health.
* We are currently reporting on weekly relative differences instead of cumulative differences to better reflect the extent of the COVID-19 pandemic as we are witnessing a decline in the reported cases. In addition, to a change in the frequency and quality of data sharing, countries started to move to weekly aggregate data and less information is shared by countries. Subscribe to the monthly infectious hazard preparedness newsletter of WHO’s Health Emergencies Programme for the latest data and analysis on epidemic- and pandemic-prone diseases, as well as news on outbreak preparedness and response within WHO’s Eastern Mediterranean Region.
Outbreak update - Cholera in Yemen, 18 August 2019
29 August 2019 - The Ministry of Public Health and Population of Yemen reported 16,296 suspected cases and 8 associated deaths during epidemiological week 33 (12- 18 August) of 2019. Thirteen percent of cases were severe. The cumulative total number of suspected cholera cases from 1 January 2018 to 18 August 2019 is 953 888, with 1323 associated deaths (CFR 0.14%). Children under five represent 24.4% of total suspected cases during 2019. The outbreak has affected 22 of 23 governorates and 305 of 333 districts in Yemen.
The trend of weekly reported suspected cholera cases started increasing from week 8 in 2019 and reached more than 29 500 cases in week 14. These were the maximum number of cases reported so far. The trend of suspected cases has been fluctuating over the past weeks. Starting from week 23, the number of cases increased with the start of rainy season. However, since week 27, less cases were reported every week. For the last three weeks, a stable trend was observed.
The governorates reporting the highest number of suspected cases of cholera during 2019 were Amanat Al Asimah (83 870), Al Hudaydah (74 547) Sana’a (72 160), Hajjah (55 272), Dhamar (50 016), Ibb (52 611), and Arman (38 916).
Of a total 88 173 samples tested since January 2019, 4352 have been confirmed as cholera-positive by culture at the central public health laboratories. During this reporting period the governorates reporting the highest number of positive culture were Taizz (1106), Amanat Al Asimah (1236) and Sana’a (436).
WHO continues to provide leadership and support for activities with health authorities and partners to respond to this ongoing cholera outbreak, including case management, surveillance and laboratory investigations, hotspot mapping and Oral Cholera Vaccine (OCV) campaign planning, water sanitation, hygiene (WaSH) and risk communication.
«القول بأن «في إمكاننا القضاء على الكوليرا» أمرٌ لا يمكن الاستخفاف به على الإطلاق»
«القول بأن «في إمكاننا القضاء على الكوليرا» أمرٌ لا يمكن الاستخفاف به على الإطلاق»
27 كانون الأول/ ديسمبر 2018 هناك خطة جديدة لمعركة القضاء على الكوليرا. فالوثيقة التي عُنوِنَت بجدارة «القضاء على الكوليرا»، تبعث على التفاؤل وتطمح إلى عالم لا يمثل فيه ذلك المرض القديم قِدَم الزمن تهديداً للصحة العامة بعد اليوم. ويقود الدكتور دومينيك ليغروس جهود منظمة الصحة العالمية للقضاء على الكوليرا، حيث كان جزءًا أصيلًا من هذه المعركة طيلة 25 عامًا. ومن الناحية التقنيّة، يقول الدكتور ليغروس إن علاج الكوليرا أمر بسيط للغاية: فهو يبدأ وينتهي بالحصول على المياه المأمونة. غير أن واقع الحال أثبت ما يكتنفه هذا الأمر من تعقيدات كبيرة.