Surveillance of NCDs

WHO supports countries in monitoring and tracking noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) through surveillance, to enhance national NCD surveillance, gather data that can be used at the national level, and evaluate progress made towards meeting regional and global NCD control and prevention targets. This includes working towards Sustainable Development Goal target 3.4, which aims to reduce premature deaths from NCDs by one third through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and wellbeing by 2030, as well as the global interim target of reducing premature deaths from NCDs by 25% by 2025.
NCD surveillance plays a crucial role in monitoring and evaluating the patterns and trends of diseases, which is essential for the better prevention and management of NCDs. By collecting data, countries can set priorities and develop targeted interventions to address the NCD pandemic. By strengthening NCD surveillance, countries can increase their efforts to control and prevent NCDs. There is an urgent need for countries to improve the coverage and quality of mortality data, conduct regular risk factor surveys on a national scale using standardized methods, and regularly assess national capacity to prevent and control NCDs. Countries should also take advantage of existing data collection efforts. In the Eastern Mediterranean Region, countries have committed to surveillance, monitoring and evaluation through the regional framework for action on the prevention and control of NCDs. WHO will continue to support countries as they strengthen their NCD surveillance efforts, and will take a step-by-step approach to building their capabilities and systems.
Commitments to strengthen NCD surveillance
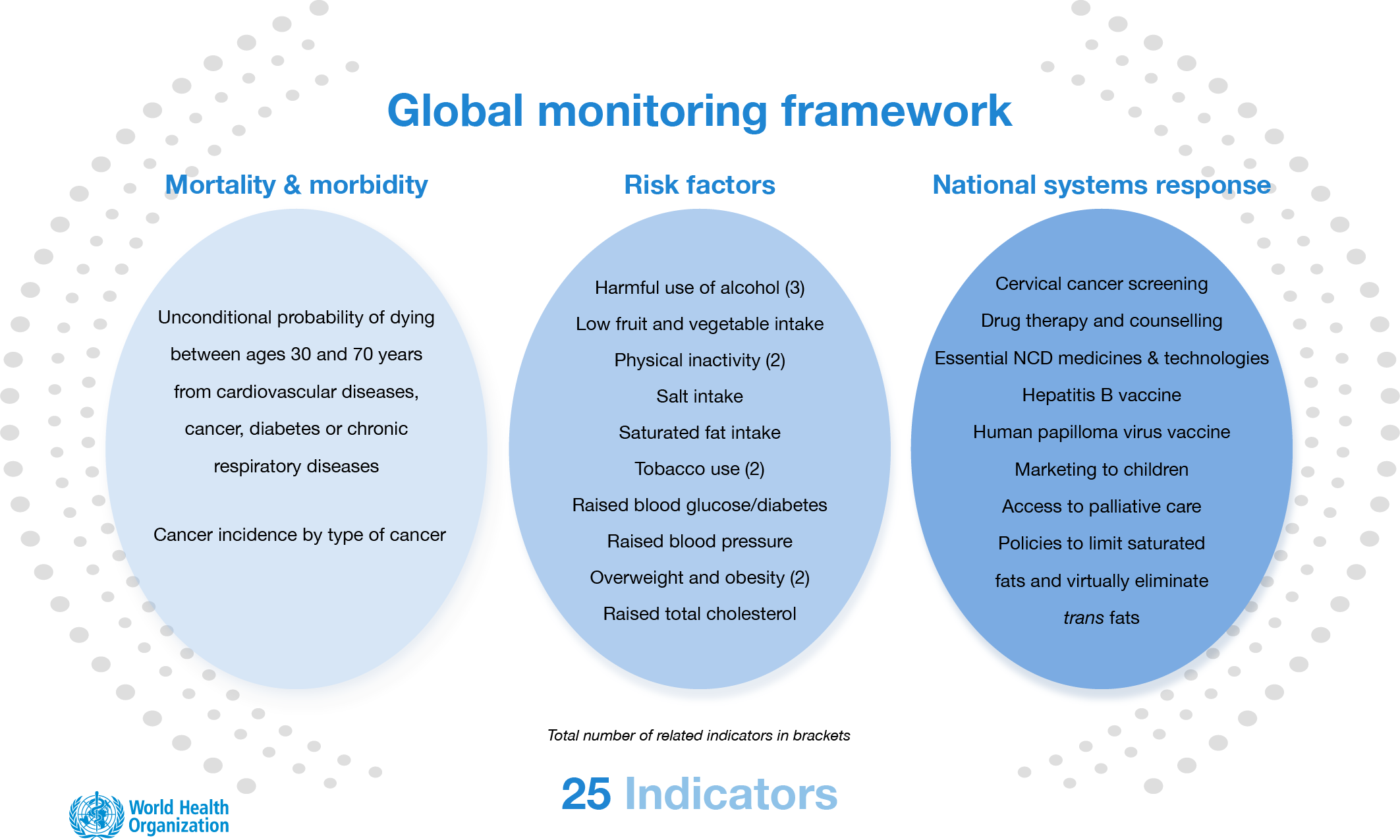
In 2013, the 66th World Health Assembly, the decision-making body of the WHO, adopted a global monitoring framework for NCDs that includes 25 key indicators to track progress in preventing and controlling NCDs. The framework includes three essential components or pillars that all countries should establish and strengthen. These components include: monitoring exposures, which refers to the surveillance of risk factors for NCDs such as tobacco use, unhealthy diet and physical inactivity; monitoring outcomes, which refers to the surveillance of morbidity and disease-specific mortality, including the incidence and prevalence of NCDs; and assessing health system capacity and response, which includes monitoring national capacity to prevent NCDs in terms of policies and plans, infrastructure, human resources, and access to essential health care including medicines. This framework is designed to help countries effectively monitor and control the NCD epidemic and improve the health of their populations. The Assembly also agreed on a set of voluntary targets to prevent and control NCDs by 2025, which are linked to the global monitoring framework. These targets include a goal to reduce premature deaths from NCDs by 25%.
The 66th World Health Assembly also endorsed the WHO global action plan for the prevention and control of NCDs 2013–2020 (extended to 2030), which is aimed at achieving the commitments made by world leaders in the September 2011 United Nations Political Declaration on the Prevention and Control of NCDs (updated in 2018). The plan is organized around six objectives, one of which is to monitor NCD trends and determinants and evaluate progress in their prevention and control through surveillance. In 2015, the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development recognized the importance of addressing NCDs by including a target to reduce premature deaths from NCDs by one third by 2030. Within the Eastern Mediterranean Region, a regional framework for action to implement the UN Political Declaration on NCDs was developed in 2012 and updated in 2019, as a roadmap for countries, providing strategic interventions and a set of indicators to assess country progress by 2030. Surveillance is a key area of the framework, to capture the magnitude and risk factors of NCDs and monitor progress.
Global monitoring framework for NCDs
Regional framework for action on the prevention and control of NCDs
NCD Data portal
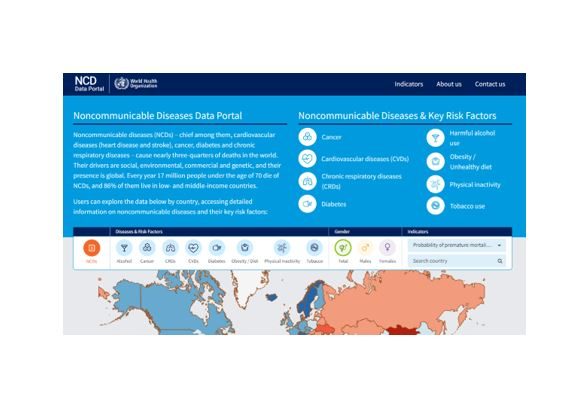
TThe noncommunicable diseases data portal aims to raise awareness on progress in tackling NCDs and their risk factors and strengthen accountability for action by countries. It displays data to highlight current status of NCD mortality, morbidity and risk factor exposures, and track global and national progress against key targets, identify common challenges, and signpost useful resources. To explore more information about the main NCDs, which include cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes and chronic respiratory diseases and their key risk factors such as unhealthy diets, tobacco use, physical inactivity and harmful use of alcohol, users can access detailed data by country below.
WHO STEPwise approach

The WHO STEPwise approach to surveillance of NCD risk factors (STEPS) is a standardized method recommended by WHO for monitoring the prevalence of chronic diseases and their risk factors. It was developed as part of a global surveillance strategy to address the need for country-specific data on NCDs. The approach uses a standardized survey instrument and methodology that can be adapted to different resource settings and helps to build capacity within countries. The data collected through STEPS not only allows for monitoring NCD trends within countries, but also facilitates cross-country comparisons by using the same standardized questions and protocols across all participating countries.
The WHO Eastern Mediterranean Region has many countries that have conducted STEPS surveys and have published their results in various forms such as country reports, data books, fact sheets, journal articles, presentations, and posters. These documents can be accessed by visiting the STEPS country data and reports page and selecting the desired country. This provides a comprehensive understanding of the NCD trends and risk factors in those countries. It is a valuable tool for monitoring the progress of NCD prevention and control in the Region.
STEPwise approach to NCD risk factor surveillance (STEPS)
STEPS country data and reports
Survey of NCD risk factors (regional factsheets)
WHO STEPwise approach to stroke surveillance
NCD Country capacity survey

WHO conducts regular assessments of countries' capacity to prevent and control NCDs through the use of the NCD Country Capacity Survey (NCD CCS). The survey is completed by national NCD focal points or designated colleagues within the Ministry of Health or a national institute/agency and covers topics such as health system infrastructure, funding, policies and strategies, surveillance, primary health care, and partnerships and collaboration. The results of the survey allow countries and WHO to monitor progress in expanding capabilities to respond to the NCD epidemic. The survey has been conducted in 2000, 2005, 2010, 2013, 2015, 2017, 2019 and 2021, and global and region-specific reports are available online.
NCD Progress monitor

WHO published a technical note in May 2015 outlining its plans to report to the United Nations General Assembly in 2017 on the progress made towards implementing national commitmentsin cluded in the 2011 UN Political Declaration and the 2014 UN Outcome Document related to noncommunicable diseases (NCDs). This technical note was updated in September 2017 to reflect updated set of WHO ‘best-buys’ and other recommended interventions for preventing and controlling NCDs that were approved by the World Health Assembly. The Progress Monitor series provides data on 19 indicators outlined in the technical note for all 194 WHO Member States. These indicators include setting timbe-bound targets to reduce NCD deaths, developing all-of-government policies to address NCDs, implementing key tobacco demand reduction measures, measures to reduce harmful use of alcohol and unhealthy diets, promoting physical activity, and strengthening health systems through primary health care and universal coverage.
PAKISTAN (GYTS) 2022 Factsheet

The Global Youth Tobacco Survey (GYTS), a component of the Global Tobacco Surveillance System (GTSS), is a global standard for systematically monitoring youth tobacco use and tracking key tobacco control indicators. GYTS is a cross-sectional, nationally representative school-based survey of students in grades associated with ages 13 to 15 years. GYTS uses a standard core questionnaire, sample design, and data collection protocol. It assists countries in fulfilling their obligations under the World Health Organization (WHO) Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) to generate comparable data within and across countries. WHO has developed MPOWER, a technical package of selected demand reduction measures contained in the WHO FCTC:
PAKISTAN (GYTS) 2022 Factsheet
Global School-based Student Health Survey
The Global School-based Student Health Survey (GSHS) is a collaborative surveillance project that helps countries measure and assess the behavioural risk factors and protective factors among young people aged 13 to 17 years in 10 key areas. This school-based survey is relatively low-cost and uses a self-administered questionnaire to obtain data on young people's health behaviour and protective factors related to leading causes of disability and death worldwide. You can find reports, factsheets and data sets from the GSHS on the data and reporting section of the WHO headquarters website. Please check that section to access the information that is available.
Global Tobacco Surveillance System
We began tracking tobacco in 1999 in collaboration with our partners, and we have maintained this practice on an ongoing basis. Our efforts have been supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta and the Canadian Public Health Association. Our aim is to monitor the trends in knowledge, attitudes, behaviours, and environmental factors related to tobacco use over time. To achieve this, we use a consistent methodology and core questionnaire across different countries, which allows us to compare data and track trends. Initially, we focused on collecting data from young people, but have since expanded our surveillance to include school personnel, health professional students and adults. Currently, our surveillance system, called the Global Tobacco Surveillance System (GTSS), consists of four separate surveys: Global Youth Tobacco Survey (GYTS); Global School Personnel Survey (GSPS); Global Health Professionals Student Survey (GHPSS); and Global Adult Tobacco Survey (GATS).
Global Tobacco Surveillance System: Two decades in review
Related resources
Importance of surveillance in preventing and controlling NCDs
NCD surveillance in the Eastern Mediterranean Region
NCDs and the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
UN Political Declaration on the Prevention and Control of NCDs